![]()
Part of the settings can also be set up with logic program I/O driver instructions.
 31.23 I/O Driver Instructions
31.23 I/O Driver Instructions
A 2-phase counter is a counter that takes two input terminals to measure the input signal of a 2-phase input.
A maximum of two 2-phase counters can be used. When you use one, you use X0 and X2 input terminals, and when you use two, you use X0 and X2 as well as X4 and X6 input terminals. Because two CH1 input terminals and two CH2 input terminals are occupied, allocated terminal arrangement differs from that of a single counter. Feature and setting methods for preload input, prestrobe input, and matching input are the same as that of a single counter.
The main functions of the 2-phase counters are indicated in the following table.
![]()
Part of the settings can also be set up with logic program I/O driver instructions.![]() 31.23 I/O Driver Instructions
31.23 I/O Driver Instructions
|
Summary of functions |
Browse to |
|
Clears the counter, which currently has an external signal value. |
|
|
Starts and stops the high-speed counter |
|
|
Checks the start and stop status of the high-speed counter |
|
|
Rewrites the current counter value |
|
|
Stores the current counter value (read) |
|
|
Outputs the current counter value when it exceeds the specified value |
|
|
Save the counter value when the logic stops |
|
As for measuring methods, there are four types of modes ranging from "Phase Counting Mode 0" to "Phase Counting Mode 3".
Mode 0 (2 Phase x 4)
When Counter A (A Phase) is ahead of Counter B (B Phase), operates as an up counter. When Counter A (A Phase) is lagging behind Counter B (B Phase), operates as a down counter.
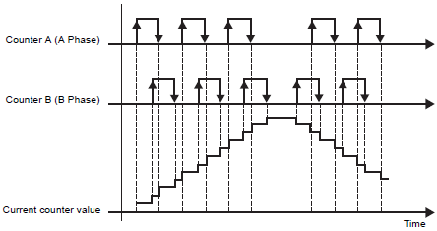
Counter A (A Phase) is ahead of Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
1 (High) |
Positive transition |
Up Count |
|
0 (Low) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
1 (High) |
|
|
Positive transition |
0 (Low) |
Counter A (A Phase) is lagging behind Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
0 (Low) |
Positive transition |
Down Count |
|
1 (High) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
0 (Low) |
|
|
Positive transition |
1 (High) |
Mode 1 (Counter + Direction)
Begins counting at the positive transition of Counter A (A Phase). If Counter B (B Phase) is 0 (Low), it counts up, if 1 (High), it counts down.
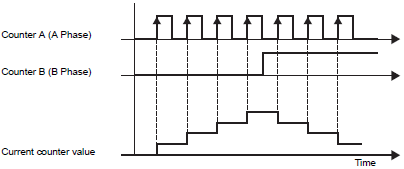
Counter A (A Phase) is ahead of Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
1 (High) |
Positive transition |
Not count |
|
0 (Low) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
1 (High) |
|
|
Positive transition |
0 (Low) |
Up Count |
Counter A (A Phase) is lagging behind Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
0 (Low) |
Positive transition |
Not count |
|
1 (High) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
0 (Low) |
|
|
Positive transition |
1 (High) |
Down Count |
Mode 2 (Up + Down)
When Counter A (A Phase) has a positive transition and Counter B (B Phase) is 0 (Low), operates as an up counter. When Counter B (B Phase) has a positive transition and Counter A (A Phase) is 0 (Low), operates as a down counter.
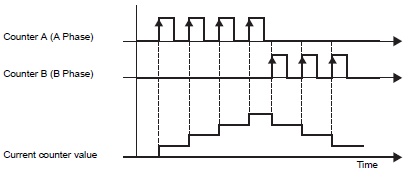
Counter A (A Phase) is ahead of Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
1 (High) |
Positive transition |
Not count |
|
0 (Low) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
1 (High) |
|
|
Positive transition |
0 (Low) |
Up Count |
Counter A (A Phase) is lagging behind Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
0 (Low) |
Positive transition |
Down Count |
|
1 (High) |
Negative transition |
Not count |
|
Negative transition |
0 (Low) |
|
|
Positive transition |
1 (High) |
Mode 3 (2 Phase x 2)
Begins counting at a Counter B (B Phase) positive or negative transition. When Counter A (A Phase) is ahead of Counter B (B Phase), it counts up. When Counter A (A Phase) is lagging behind Counter B (B Phase), it counts down.
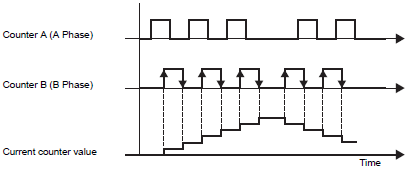
Counter A (A Phase) is ahead of Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
1 (High) |
Positive transition |
Up Count |
|
0 (Low) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
1 (High) |
Not count |
|
Positive transition |
0 (Low) |
Counter A (A Phase) is lagging behind Counter B (B Phase)
|
Counter A (A Phase) |
Counter B (B Phase) |
Operations |
|
0 (Low) |
Positive transition |
Down Count |
|
1 (High) |
Negative transition |
|
|
Negative transition |
0 (Low) |
Not count |
|
Positive transition |
1 (High) |
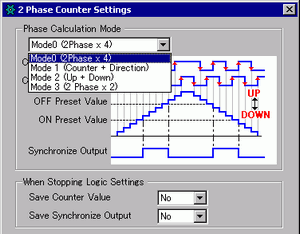
Phase Calculation Mode Settings
In [System Settings] select [I/O Driver].
On the [Internal Driver 1] screen, select the [2 Phase Counter] check box and click [2 Phase Counter Settings].
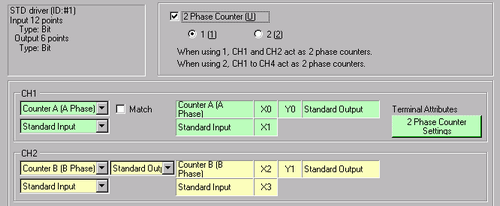
The [2 Phase Counter Settings] dialog box appears. Select the phase calculation mode from the pull-down menu.