
Label Settings
![]() 22.11.3.1 Label Settings
22.11.3.1 Label Settings
Set from the Control, Status, Receive Data Count, Receive Function, and Send functions.
Receive
![]() 22.11.3.2 Receive
22.11.3.2 Receive
Reads received data from the designated serial port, such as COM1.
Send
![]() 22.11.3.3 Send
22.11.3.3 Send
Writes to the designated serial port, such as COM1.
Extended Receive
![]() 22.11.3.4 Extended Receive
22.11.3.4 Extended Receive
Reads received data from the designated serial port, such as COM1.
It can only be used in an Extended Script.
Extended Send
![]() 22.11.3.5 Extended Send
22.11.3.5 Extended Send
Writes to the designated serial port, such as COM1.
It can only be used in an Extended Script.
Standby Reception
![]() 22.11.3.6 Standby Reception
22.11.3.6 Standby Reception
Stays in standby receive mode until it receives specified text.
It can only be used in an Extended Script.
Standby
![]() 22.11.3.7 Standby
22.11.3.7 Standby
The system waits the specified period of time.
It can only be used in an Extended Script.
![]()
Label Settings, Send, and Receive can be easily included in a D-Script/Global D-Script.
To communicate with D-Scripts/Global D-Scripts, set the following script settings. If script settings are not designated, they cannot execute.
Script Settings in D-Script/Global D-Script
In [System Settings], click [Script].
Set the [Type] to [D-Script/Global D-Script].
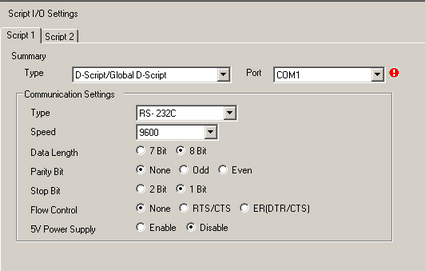
There are two tabs for the script settings. The above example uses [Script1].
Set the [Port] to COM1 or COM2, and set the [Communication Settings] to match the Extended SIO.
When creating a communication program with more advanced functionality than the SIO port operation, it is recommended to use an [Extended Script]. See the following for examples on how to use extended scripts, 22.5 Communicating with Unsupported Peripheral Devices.
If you do not want to perform flow control between the display unit and the device/PLC, initiate communication from the display unit after starting up. Otherwise it may cause a communication error.