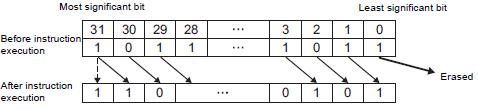
When the SAR or SARP instruction is executed, the S1 bits are shifted to the right of the S2 number of bits. For each bit shift, the bottom-most bit (the least significant bit) is lost, and the most significant bit is stored in the topmost empty bit. The result is stored in D1. The SAR and SARP instructions always pass power. When using the SAR and SARP instructions, an error will occur if the variables specified in operands S1 and D1 are not the same type. Designate the same variable type in operands S1 and D1.
Refer to the following for specifying a constant.
S1: Shift Address
Specify the address to shift.
S2: Number of bits to shift
Specifies the number of bits to shift.
D1: Storage address
Specifies the address to store the shift result.
For example, when 1 bit is shifted to the right

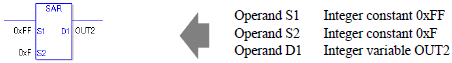
When operand D1 is an integer variable

When operand D1 is an integer variable and you want to input hexadecimal values in operands S1 and S2.
When 0x (zero and lower case "x") is input, the following values become hexadecimal values.
When specifying an array variable, specify an array element.
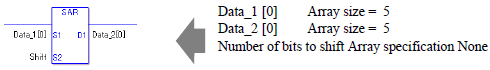
31 array element bits are shifted. For S2, specify a value between 0 and 31.